40 heatmap 2 row labels
heatmap function - RDocumentation A heat map is a false color image (basically image (t(x)) ) with a dendrogram added to the left side and to the top. Typically, reordering of the rows and columns according to some set of values (row or column means) within the restrictions imposed by the dendrogram is carried out. Chapter 2 A Single Heatmap | ComplexHeatmap Complete Reference 2 A Single Heatmap. A single heatmap is the most used approach for visualizing data. Although “the shining point” of the ComplexHeatmap package is that it can visualize a list of heatmaps in parallel, however, as the basic unit of the heatmap list, it is still very important to have the single heatmap well configured.
seaborn.heatmap — seaborn 0.12.0 documentation - PyData If True, plot the column names of the dataframe. If False, don’t plot the column names. If list-like, plot these alternate labels as the xticklabels. If an integer, use the column names but plot only every n label. If “auto”, try to densely plot non-overlapping labels. mask bool array or DataFrame, optional

Heatmap 2 row labels
18.1 heatmap.2 function from gplots package | Introduction to R The heatmap.2 function from the gplots package allows to produce highly customizable heatmaps. # install gplots package install.packages ( "gplots" ) # load package library ( "gplots" ) # make matrix mat <- matrix ( rnorm ( 1200 ), ncol= 6 ) # heatmap with the defaults parameters heatmap.2 ( x= mat) Building heatmap with R – the R Graph Gallery How to do it: below is the most basic heatmap you can build in base R, using the heatmap() function with no parameters. Note that it takes as input a matrix. If you have a data frame, you can convert it to a matrix with as.matrix(), but you need numeric variables only. How to read it: each column is a variable. Each observation is a row. Visualizing distributions of data — seaborn 0.12.0 documentation This plot immediately affords a few insights about the flipper_length_mm variable. For instance, we can see that the most common flipper length is about 195 mm, but the distribution appears bimodal, so this one number does not represent the data well.
Heatmap 2 row labels. Visualizing distributions of data — seaborn 0.12.0 documentation This plot immediately affords a few insights about the flipper_length_mm variable. For instance, we can see that the most common flipper length is about 195 mm, but the distribution appears bimodal, so this one number does not represent the data well. Building heatmap with R – the R Graph Gallery How to do it: below is the most basic heatmap you can build in base R, using the heatmap() function with no parameters. Note that it takes as input a matrix. If you have a data frame, you can convert it to a matrix with as.matrix(), but you need numeric variables only. How to read it: each column is a variable. Each observation is a row. 18.1 heatmap.2 function from gplots package | Introduction to R The heatmap.2 function from the gplots package allows to produce highly customizable heatmaps. # install gplots package install.packages ( "gplots" ) # load package library ( "gplots" ) # make matrix mat <- matrix ( rnorm ( 1200 ), ncol= 6 ) # heatmap with the defaults parameters heatmap.2 ( x= mat)




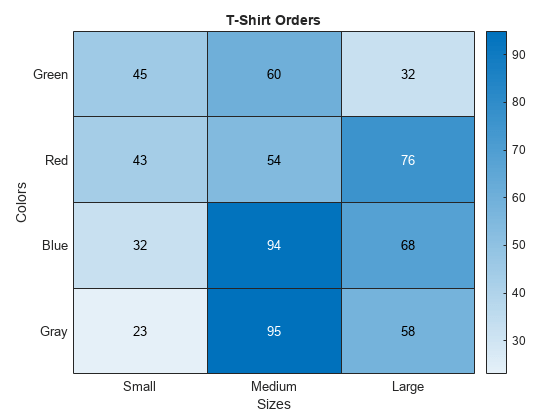





Post a Comment for "40 heatmap 2 row labels"